Using Baidu: China’s Largest Search Engine
 By: Rebecca Li
By: Rebecca Li
KoMarketing Associates
The Chinese online market has been growing significantly, but until recently remained unnoticed by most Western observers. By the time Western countries started paying attention, China had already become the country with the most internet users in the world. By the end of June 2014, China had 632 million Internet users, an increase of 14.42 million from 2013. The number of search engine users in China had reached 507 million, 63 percent of which are using Baidu, China’s largest search engine.
By taking a closer look at the latter statistic, we can assume there are about 320 million search engine users advertising on Baidu, a number that roughly equates to the population of the United States.
Baidu is ranked as the number four most visited website in the world by Alexa.com and holds the second largest share of the global desktop search engine market.
Already at 63 percent of China’s market, Baidu’s portion of pie is continually growing. Based on a Search Engine report from CNNIC, around 97 percent of Chinese Internet users accessed Baidu at least once in the past six months. As a result, Baidu has run far ahead of its closest Chinese competitors, such as Google HK, Sougou, and 360.
Using Baidu to Overcome Cultural and Language Barriers
Baidu claims that it is the best Chinese search engine on their company website, not only because they know Chinese better, but also because they know Chinese audiences better.
“Just to cite one example, we believe there are at least 38 ways of saying “I” in the Chinese language. It is important that we recognize these nuances to effectively address our users’ requests. ”
![]() RELATED: Further Liberalization E-commerce in Shanghai FTZ
RELATED: Further Liberalization E-commerce in Shanghai FTZ
One can see this concept when performing an English search query on Baidu. Baidu doesn’t index many non-Chinese pages, so when you search for English terms, the user will find mostly results that are relevant for Chinese users.
For example, when users search “iWatch” on Baidu, it shows 1,980,000 relevant search results, most of which are news or pricing websites, yet Apple’s website isn’t even shown on the first page.
However, if the user searches the same phrase on Google.hk, it will show 12,100,000 search results, a much larger total than on Baidu with English pages. Often the brand page is in the first position.
This is because most of the Baidu users are in China and Baidu believes it would be more valuable to provide search results that meet the specific needs of Chinese users. As a result, websites in Chinese and hosted inside China would be ranked higher.
Companies intending to market their products in China would therefore be well advised to have a landing page in simplified Chinese, the type of Chinese characters that are used in Mainland China.
Reaching the Chinese Consumer through Baidu
Similar to Google, one can also use paid ads as an effective way to enhance brand recognition and reach target audiences in China. However, there is a significant difference between Google and Baidu on the search engine results pages (SERPs). Visitors will typically only see three paid ads on the left side of a Google SERP, yet Baidu will show many more. For example, when searching for “plane ticket,” the user will see twelve advertising links on the right-hand side.
Opinions vary on the high number of ad listings on Baidu, but the company considers it the most convenient way for users to get what they are searching for.
In China, customers are cautious of shopping online due to the prevalence of counterfeit and fake goods in the market. A consumer search engine usage report from the Chinese Internet Network Information Center shows that Internet users have low trust levels when it comes to online advertising. However, 76.8 percent of users express that they will go ahead with a purchase if the products have higher approval from previous buyers, and 72.2 percent of users trust advertising from famous brands or companies.
![]() RELATED: Trends in China’s E-Commerce Market
RELATED: Trends in China’s E-Commerce Market
To solve this problem, Baidu provides verification for all their advertisers. By verifying, Baidu gives assurance to its users that its paid ad listings are all genuine, quality businesses. This increases the likelihood that they would purchase from one of those sites, more so than an organic listing.
The screenshot below shows that Baidu provides a quality score for verified advertisers. Internet users can hover their mouse over the V symbol to see how the company scores on categories like reputation, website security or transaction security.
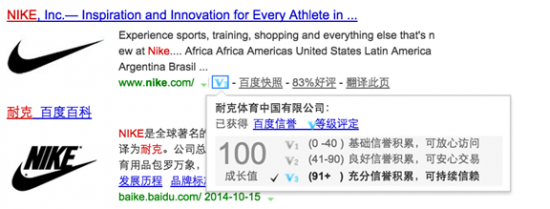
This verification process is done at the beginning of setting up a paid account, which makes the setup process slightly more complicated than Google.
One of the major differences between Google and Baidu is that Baidu favors its own platforms over regular search. For example, many Baidu search queries will show links to Baidu Tieba, the largest Chinese language community forum; Baidu Baike, a Wikipedia-like online encyclopedia; and Baidu Zhidao, the world’s largest Chinese knowledge sharing platforms, similar to answers.yahoo.com.
Baidu SEO Tools
Similar to Google, Baidu provides free analytics tools for webmasters to analyze their efforts:
- Baidu Tongji: Baidu’s web statistics tracking system.
- Baidu Zhishu (Baidu Index): It shows the search trends of selected keywords by indicating the “media exposure” and “users interests”.
Compared to only 130 million mobile search users in US, the number of mobile search users reached 406 million by the end of June 2014 in China. In general, the number of Chinese mobile Internet users now totals 527 million, which accounted for 83 percent of Chinese internet users. In China, the number of people who access the web on smart phones has now surpassed those who access the web via PC (81 percent).
Baidu predicted this trend a long time ago and started its transition to mobile in 2014. Today, Baidu has captured 80% of China’s mobile-search market share. At the same time, close to 90 percent of Baidu’s PC users have switched to its mobile apps.
This goes to say that foreign companies looking to market to the Chinese consumer will need to pay particular attention to having a mobile friendly online presence.
|
KoMarketing seeks to drive results with efficiency, embracing and seeking to stimulate change, and continually acquire and share knowledge. Our programs in search, social, and content marketing revolve around your business strategy. We execute with honesty and integrity, seeking to get better everyday. Asia Briefing Ltd. is a subsidiary of Dezan Shira & Associates. Dezan Shira is a specialist foreign direct investment practice, providing corporate establishment, business advisory, tax advisory and compliance, accounting, payroll, due diligence and financial review services to multinationals investing in China, Hong Kong, India, Vietnam, Singapore and the rest of ASEAN. For further information, please email china@dezshira.com or visit www.dezshira.com. Stay up to date with the latest business and investment trends in Asia by subscribing to our complimentary update service featuring news, commentary and regulatory insight.
|
![]()
China Investment Roadmap: The Entertainment Industry
In this special edition China Briefing Industry Report, we cast our gaze over the broad landscape of China’s entertainment industry, identifying where the greatest opportunities are to be found and why. Next, we detail some of the most important issues for foreign investors to be aware of, including legal, regulatory, and tax considerations specific to the industry. Lastly, we provide an insider analysis of the sector’s unique HR & payroll challenges.
 Employing Foreign Nationals in China
Employing Foreign Nationals in China
In this issue of China Briefing, we have set out to produce a guide to employing foreign nationals in China, from the initial step of applying for work visas, to more advanced subjects such as determining IIT liability and optimizing employee income packages for tax efficiency. Lastly, recognizing that few foreigners immigrate to China on a permanent basis, we provide an overview of methods for remitting RMB abroad.
 Tax, Accounting, and Audit in China 2015
Tax, Accounting, and Audit in China 2015
This edition of Tax, Accounting, and Audit in China, updated for 2015, offers a comprehensive overview of the major taxes foreign investors are likely to encounter when establishing or operating a business in China, as well as other tax-relevant obligations. This concise, detailed, yet pragmatic guide is ideal for CFOs, compliance officers and heads of accounting who must navigate the complex tax and accounting landscape in China in order to effectively manage and strategically plan their China operations.
- Previous Article
- Next Article What Google’s China Ban Means For Dot CN Domain Users






























