Tax-Exempt Fringe Benefits for Expatriates in China Extended till End of 2027
UPDATE (August 31, 2023): On August 18, 2023, the Ministry of Commerce (MOF) and State Taxation Administration (STA) jointly released the Announcement on the Continuation of Implementation of Individual Income Tax Preferential Policies Such as for Foreign Nationals’ Benefits (MOFCOM STA Announcement [2023] No.29). The Announcement officially extended the preferential individual income tax (IIT) policy on foreigners’ fringe benefits, which was set to expire on December 31, 2023, for another four years to December 31, 2027. This came at the same time when China extended another preferential tax policy, for the annual one-time bonus of both foreign and Chinese resident taxpayers and the GBA IIT subsidy, to the same date – December 31, 2027. We have also published a recent article here: China’s IIT Preferential Policy for Expatriates Extended to End of 2027: Key Points.
UPDATE (December 31, 2021): The government has extended the preferential IIT policy on foreigners’ fringe benefits to the end of 2023. Previously, from 2022, foreigners working in China were to lose some tax-free fringe benefits (for example, housing rental, children’s education costs, and language training costs). This would have resulted in larger tax liability for some higher-earning foreign workers. See Announcement No. 43 of 2021 of the Ministry of Finance and the State Administration of Taxation here. We have also published a recent article here: China’s IIT Preferential Policy for Expatriates Extended to End of 2023: Key Points.
Expatriates working in China enjoy various tax-exempt “benefits-in-kind” (BIK) – sometimes referred to as tax-exempt “benefits” or non-taxable “fringe benefits” (BIK are additional compensation, not included in the salary or wages, but paid on a reimbursement and non-cash basis).
However, due to the implementation of the Amended PRC Individual Income Tax (IIT) Law and relevant regulations from January 2019, certain non-taxable BIK will be replaced by additional itemized deductions for some expatriates, while other non-taxable BIK might cease to be exempt from IIT from next year.
The policy change has sparked concerns among foreign individuals as well as their employers, who may face an increase of tax burdens or labor costs. This article explains the implications of the changed policy and provides suggestions from tax, HR, and legal perspectives.
What are the tax-exempt benefits-in-kind for expatriates in China?
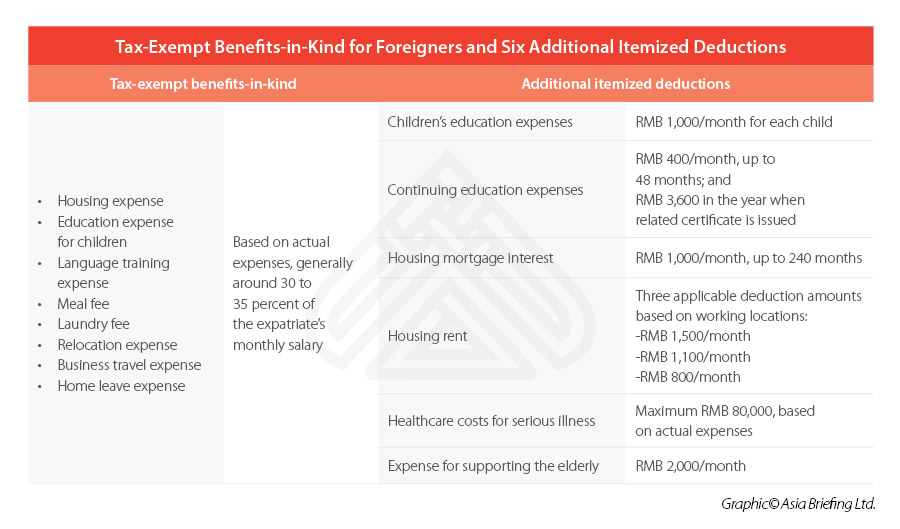
Non-China domiciled individuals working in China can currently enjoy tax-exempt benefits-in-kind, including the below eight categories:
- Housing expense
- Education expense for children
- Language training expense
- Meal fee
- Laundry fee
- Relocation expense
- Business travel expense
- Home leave expense
Such benefits-in-kind could be exempt from PRC IIT provided that the expenses are reasonable in amount and there are corresponding supporting documents, such as invoices (fapiao), for each expense. In addition, there are some specific requirements for each category. For example, for home leave expenses, only the travel expenses for the expatriate themself from China to their/spouse’s home country for up to two trips per year could be exempt from IIT.
Three-year transition period for non-China domiciled tax residents
However, with the country’s new IIT Law taking effect from January 1, 2019, the government has considered rolling back the tax exemption on special benefits-in-kind for foreigners, partly in a move to equalize benefits between local and foreign tax resident workers.
To ensure a smooth policy transition, at the end of 2018, the Ministry of Finance and the State Tax Administration jointly announced the Notice on the Preferential Policy Convergence Problem (Cai Shui [2018] No.164).
The Notice introduced a three-year transition period. From January 1, 2019 to December 31, 2021, non-China domiciled tax residents (who do not have a domicile in China and live for 183 days or more in China in a given tax year) can choose to enjoy:
- The tax-exempt benefits-in-kind; or
- The six additional itemized deductions.
To be specific, the six additional itemized deductions include:
- Children’s education expenses
- Continuing education expenses
- Housing mortgage interest
- Housing rent
- Healthcare costs for serious illness
- Expenses for taking care of the elderly
The two policies cannot be simultaneously enjoyed by non-China domiciled tax residents during the transition period. And once decided, non-China domiciled tax residents cannot change their preference within a given tax year.
According to the Notice, after the three-year transition period, that is starting January 1, 2022, non-China domiciled tax residents will no longer enjoy preferential tax-exemption policies on benefits-in-kind, including housing, language training, and children’s education.
Instead, the three categories of benefits-in-kind will be replaced by the corresponding additional itemized deductions (that is, housing rent, continuing education expenses, and children’s education expenses).
However, as to the remaining five categories of benefits-in-kind (namely meal fee, laundry, relocation expense, business travel expense, and home leave expense), the policy has not clarified whether they may continue to be tax-exempt.
“Given the possibility that the government may abolish the tax exemptions on all of the eight benefits-in-kind, or the tax bureau may become more rigorous in approving the tax exemptions on the remaining items, employers should prepare for possible changes as early as possible to avoid concerns from expatriates,” said David Niu, Senior Manager in the Human Resources Administration and Payroll Services team at Dezan Shira & Associates’ Beijing office.
Compared with the six additional itemized deductions, the eight tax-exempt benefits-in-kind are believed to be more beneficial to expatriates who have a higher income and level of expense.
The tax-exempt benefits-in-kind are deducted based on the actual cost of each expenditure, although the amount is subject to the limit of a “reasonable” amount, which is based on the local living standard, consumption level, market price, etc., and, a proportion of around 30 to 35 percent of the expatriate’s monthly salary is usually acceptable by the tax authority.
However, most additional itemized deductions (except for healthcare costs) are deducted based on a standard basis.
For example, the itemized deduction standard for children’s education fee is RMB 1,000 a child per month – this can be a much smaller amount than the foreigner’s actual expenses for children’s education.
Adam Livermore, Partner at Dezan Shira & Associates, thinks foreigners with children in international schools can be relatively more affected. “The international school tuition can come to tens of thousands of dollars per child per year. Once the children’s education expense loses tax-exempt status, expatriates with children in such schools will face a significantly higher overall tax burden,” he explained.
“Expatriates that earn enough money to put themselves into the 35 or 40 percent incremental tax bracket with a couple of kids at international school would face several thousand dollars of additional taxation. So, it is an issue for them, in terms of a lifestyle choice,” he said.
Nevertheless, the policy transition is not necessarily a bad thing for all foreigners.
Previously, to enjoy the tax-exempt benefit-in-kind, expatriates have been required to provide corresponding invoices or receipts every month for each expense, which is not easy in all circumstances.
For instance, if a foreigner wants to claim rent expense, it is not enough to simply sign a lease contract with the landlord. To get an invoice for the rent, the expatriate needs to ask the landlord to make record-filing for the lease contract and provide an invoice every month. In practice, some people try to skirt this process by using alternative invoices, which is not advisable in terms of compliance.
In addition, foreigners whose income is not that high and cannot enjoy the tax-exempt benefits-in-kind, will now be able to access the six itemized deductions as long as they are resident taxpayers. Foreign employees can claim itemized deductions directly through their tax filing or via their employer, once they obtain their tax ID in the tax bureau. The application process will be much easier than submitting a pile of invoices or receipts.
Preparing for possible transition
As the policy change could result in some expatriate employees facing a reduction of up to 13 percent in their net take-home pay, to ensure staff stability, it is highly advisable that employers re-examine the labor contracts with affected employees and consider restructuring the employee’s salary package to lower their tax burden. Early communication and planning can improve transparency and avoid any disputes.
In some circumstances, enterprises may need to compensate foreign employees for their increased tax burden. “For larger multinationals, I don’t think this will be a big burden. But it could be significant for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs), especially those that are already struggling to cover the costs of multiple expatriates in China out of operating profit being made there,” according to Livermore who added, “these companies might need to adjust their model, for example, considering hiring more ‘in-pats’.”
Large multinational companies (MNCs) may face the increased budget cost of dispatching personnel in China. “For the sake of cost control, the headquarters of these companies will need to be more prudent and agile in planning the dispatching of employees to China,” Livermore advised.
David Niu also added: “In fact, some regions of China have been introducing preferential IIT policies to reduce the tax burden on foreign talents. For example, relocation to Greater Bay Area has become a strategy for some multinationals”.
Currently, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area offers IIT subsidies to “high-end” and “urgently needed” foreign talents (including those from Hong Kong, Macao, and Taiwan), which can substantially lower their IIT rate to 15 percent until the end of 2023. To be eligible, however, the foreign worker has to work in the designated nine cities in Guangdong province and meet the definition of “overseas talent” and “high-end talent” or “talent in short supply”. Moreover, the foreign worker must satisfy some basic conditions and requirements on contract terms and income, as set out by the municipal governments.
Hainan Free Trade Port also introduced a similar IIT preferential policy for “high-end” and “urgently needed” foreign and domestic talents until the end of 2024. Hainan will require foreign individuals to sign a labor contract of more than one year with an enterprise registered and having substantial operations in Hainan FTP, in order to benefit from the lower IIT rate in certain sectors. From 2025 to 2035, Hainan FTP will continue to reduce IIT rates to 3, 10, and 15 percent (three tax brackets) for eligible talents’ taxable income earned in Hainan, but qualified foreign or Chinese talents have to reside there for no less than 183 days per year.
“Other regions may also consider similar policies so as to stay competent in attracting talents,” Niu said. Stakeholders can pay close attention to relevant information or contact local experts.
With a large professional team of tax, HR, and legal experts located throughout China, Dezan Shira & Associates has been providing professional human resources, payroll, tax, legal advisory services, and China individual income tax briefing for our clients. For more information and assistance on salary structure adjustment, labor contract modification, and staff re-allocation, you are welcome to consult our experts and email us at China@dezshira.com.
This article was originally published April 14, 2021. An update was inserted on December 31, 2021 as the preferential IIT policy on foreigners’ fringe benefits has been extended to the end of 2023.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China’s IIT Preferential Policy for Expatriates Extended to End of 2027: Key Points
- Next Article China’s Data Center Sector: Industry and Regulatory Insights