China Expatriate Annual Income Tax Reporting for 2010 Tax Year
Update (January 15, 2013): For information regarding expatriate income tax filing for the 2012 tax year, please click here.
Jan. 18 – Individuals residing in China are subject to individual income tax (IIT). Expatriates who are employed in China are liable for IIT from either the first day they arrive in China or their first official working day. Be aware that the China Tax Bureau may take the arrival date as the trigger point for tax liabilities. They must file a monthly tax return as well as an additional annual return. Penalties for late filing can be up to five times the amount that was due.
Tax liabilities of foreigners generally depend on the period of time an individual spends in China and the source of income. Individuals who spend less than 90 days in one calendar year in China are exempt from IIT if the employment income is paid by an overseas entity.
Residents of countries that have signed a double taxation treaty with China may stay in China for up to 183 days (instead of 90 days) without facing any tax obligations in this case.
If an individual is paid by a China entity, any income derived from working in China will be taxable.
Individuals who stay in China for more than 90 (183) days, but less than a year, are subject to personal income tax on their employment income derived from work performed in China – regardless of which entity is paying.
Individuals who reside in China for more than one year, but less than five years, are subject to personal income tax on both China-sourced and foreign-sourced income borne by a China-based entity. Foreign individuals who reside in China for more than five years are taxed on their worldwide income.
A foreign individual who holds the position of legal or chief representative of a China-based entity is automatically liable for paying income tax also on employment income derived from work performed outside China and paid by the China-based entity.
IIT rates for employment
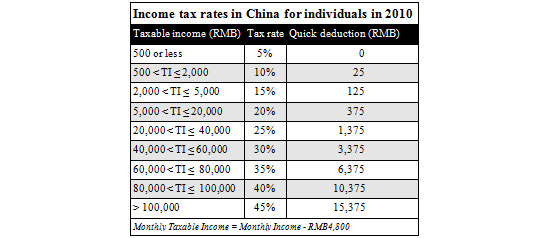
Income from wages and salaries is taxed according to the following progressive rates, ranging from 5 percent to 45 percent. Monthly taxable income is calculated after a standard monthly deduction of RMB2,000 for local employees. For foreign individuals working in China (including residents of Hong Kong, Taiwan and Macau), the standard monthly deduction is RMB4,800.
Tax Payable = Taxable Income x Applicable Tax Rate – Quick Calculation Deduction
If the individual income tax is borne by the employer, a different tax rate table will be used to reflect the tax-on-tax effect.
Employment benefits
For IIT purposes, taxable income refers to “wages, salaries, bonuses, year-end bonus, profit shares, allowances or subsidies or other income related to job or employment.”
Certain employment benefits for foreign individuals could be specifically treated as not being taxable under the IIT law if certain criteria can be met. These include:
- Employee housing costs (with supporting invoices)
- Reasonable home leave fares of two trips per annum for the employee (with supporting invoices)
- Reasonable employee relocation and moving costs (with supporting invoices)
- Reasonable reimbursement of certain meals, laundry, language training costs and children’s education expenses in the PRC (with supporting invoices)
- Any cash allowance paid to cover expected work-related expenditures (such as an entertaining or travel allowance) will be fully taxable to an employee. IIT may be reduced by reimbursing specific work-related expenses incurred by an employee (which may include entertainment, health or social club fees, local travel, newspapers and journals, telephone costs, etc.) instead of paying an allowance. The expense reimbursement may not be subject to IIT if prescribed administrative procedures are followed.
IIT rates for income other than employment income
Proprietors; contracting and leasing
Operating profit of individual industrialists and merchants’ production and business operations or from the contracting or leasing of operations of enterprises and institutions is subject to tax at progressive rates ranging from 5 percent to 35 percent. The 35 percent marginal rate applies to annual taxable income (gross revenue less allowable costs, expenses and losses) over RMB50,000.
Income of authors
Such income is taxed at a flat rate of 20 percent, applied to 70 percent of gross.
Compensation for personal services
Such income is taxable at 20 percent if the taxable income (after allowable deductions) from a single payment does not exceed RMB20,000; 30 percent for the portion over RMB20,000 but not exceeding RMB50,000; and 40 percent for the portion exceeding RMB50,000.
Royalties, interest, dividends, leases on or assignment of property, other income
Such income is taxed at a flat rate of 20 percent.
Allowable deductions
On income from the contracting and leasing of operations of enterprises and institutions, a monthly deduction of requisite expenses of RMB2,000 is allowed. On income from compensation for personal services, royalties, or leases on property, a deduction of RMB800 is allowed if the income received in a single payment is less than RMB4,000. If the income received in a single payment is more than RMB4,000, a 20 percent deduction is allowed. No deduction is allowed against income from interest, dividends, bonuses or other income. For transfers of property, the original cost plus reasonable expenses are deductible.
Tax filing and payment
IIT is normally withheld from wages or salaries by employers and paid to the tax authorities on a monthly basis. Individual income tax returns must be filed within seven days following the end of each month.
Annual IIT self reporting requirement
Taxpayers who meet one the following five conditions should file self-declarations of individual income taxes.
- An annual income of more than RMB120,000
- Income derived from two or more places inside the People’s Republic of China
- Income derived partly or fully from sources outside the People’s Republic of China
- Have received taxable income but not paid tax
- Other conditions regulated by the State Council
Information included in the IIT declaration form
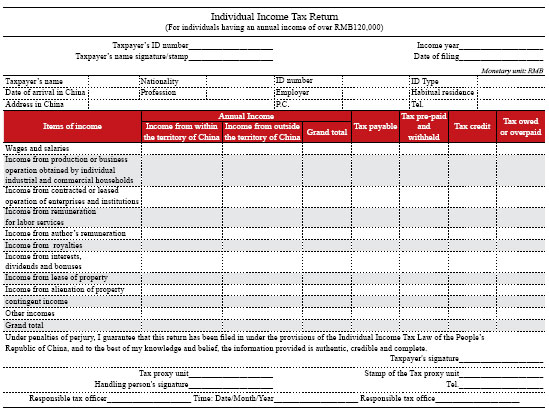
Important information that should be included in the IIT declaration form includes: name, ID type and number, profession, employer, place of residence, address in China, post code and telephone number, as well as tax data such as the annual amount of any different sourced incomes, taxes payable, taxes prepaid and withheld, foreign tax credit and taxes owed or overpaid. In addition, foreigners should declare their nationality and date of arrival in China.
Expatriates in China requiring assistance with their annual returns may contact Dezan Shira & Associates at tax@dezshira.com. The firm’s brochure can be downloaded here.
Parts of this article were taken from the January/February issue of China Briefing Magazine.
Related Reading
 Annual Compliance and Audit for Expatriates and Foreign Investors in China
Annual Compliance and Audit for Expatriates and Foreign Investors in China
In this issue of China Briefing we discuss expatriate individual income tax filings together with permissible tax deductions and allowances.
 The China Tax Guide (2010, fifth edition)
The China Tax Guide (2010, fifth edition)
A comprehensive overview of all the taxes foreign investors are likely to encounter when establishing or operating a business in China. (PDF priced at US$40)
- Previous Article China Introduces Consumption Tax Exemption for Biodiesel Production
- Next Article China Meets Energy Consumption Target for 2010