Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025: Trends and Opportunities
China has unveiled the latest Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025 after launching another round of its “Go West” campaign, in a bid to lure investment into its vast western region. Eligible companies can enjoy lower corporate income tax rates. The Western region is also acquiring strategic importance as China seeks to enhance the construction of the Belt and Road and cement its position in global supply chains.
On November 29, 2024, the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC) released the Catalogue of Encouraged Industries in Western China (2025 Edition) (hereinafter referred to as the Encouraged Catalogue for Western China), which will take effect on January 1, 2025. It will repeal the 2020 Edition simultaneously.
Under the current policy, eligible companies established and operating in western China can benefit from a reduced corporate income tax (CIT) rate of 15 percent, compared to China’s standard CIT rate of 25 percent. To qualify, a company’s primary business must fall under one of the categories listed in the Encouraged Catalogue for Western China, and revenue from this business must account for at least 60 percent of the company’s total revenue. This preferential policy will remain in effect until the end of 2030.
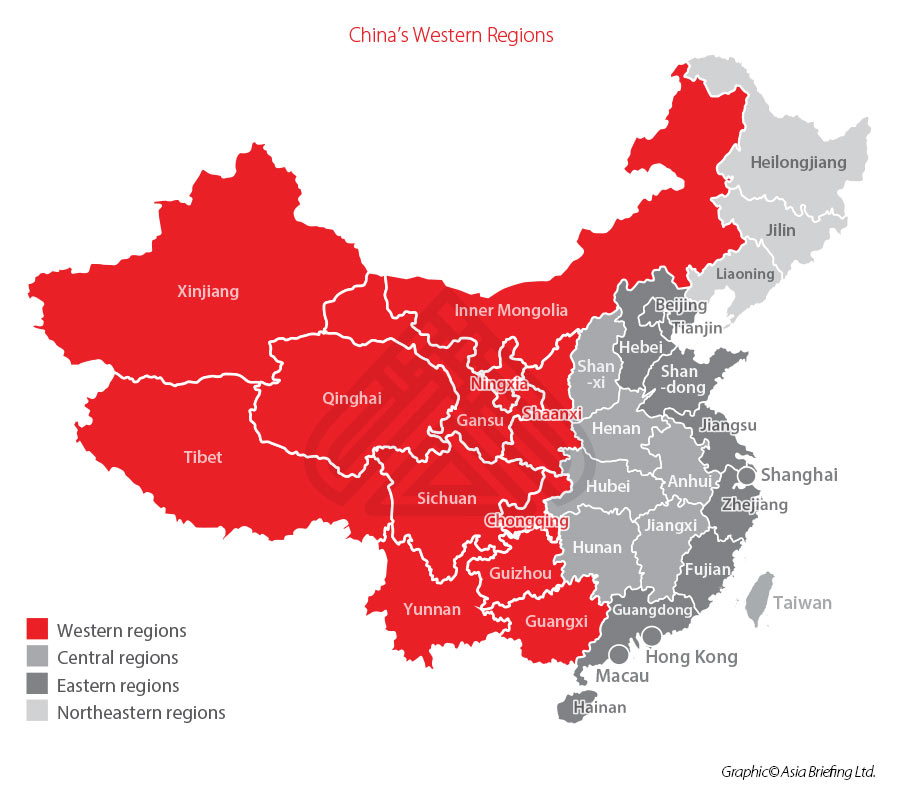
What are the western regions of China?
The western regions include 12 provinces – Inner Mongolia, Guangxi, Chongqing, Sichuan, Guizhou, Yunnan, Tibet, Shaanxi, Gansu, Qinghai, Ningxia, and Xinjiang, which cover more than 70 percent of the country’s land area and have nearly a third of its population. Some cities or regions in other provinces, such as Xiangxi of Hunan, Enshi of Hubei, Yanbian of Jilin, and Ganzhou of Jiangxi are also within the scope of applying the Encouraged Catalogue for Western China.
What is in the Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025?
The Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025 includes two parts:
- Encouraged industries as detailed in the existing national industry catalogues, such as the Catalogue for Guiding Industry Restructuring and Catalogue of Encouraged Industries for Foreign Investment; and
- A list of newly added encouraged industries in the Western Region, which applies only to domestic companies.
Foreign-invested enterprises (FIE) will need to follow the Catalogue of Encouraged Industries for Foreign Investment.
The Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025 includes 564 encouraged industries, representing a net increase of 29 categories compared to the 2020 edition. The newly added industries emphasize alignment with local economic strengths and emerging market trends, such as specialized agriculture and animal husbandry, electronics, resource processing, and equipment manufacturing.
Below we summarize some major encouraged industries in each Western province:
| Province | Major encouraged industries (non-exclusive) |
| Chongqing |
|
| Sichuan |
|
| Guizhou |
|
|
|
| Tibet |
|
| Shaanxi |
|
| Gansu |
|
| Qinghai |
|
| Ningxia |
|
| Xinjiang |
|
| Inner Mongolia |
|
| Guangxi |
|
The full list can be found here.
These updates align with China’s broader national goals for high-quality development as outlined during the Third Plenary Session of the 20th CPC Central Committee. By continuing to support industrial upgrading, economic diversification, and sustainable growth, the policy aims to enhance the Western region’s role as a hub for strategic industries, further cementing its position as a key driver of China’s economic future.
Do companies established by foreign-invested enterprises (FIEs) within China qualify for the CIT incentives for Western China?
The classification of enterprises established by FIEs through reinvestment in China depends on specific circumstances. Enterprises established by foreign-invested holding companies, foreign-invested venture capital enterprises, or foreign-invested partnerships primarily engaged in investment activities are classified as FIEs. However, enterprises established by other types of FIEs in China are classified as domestic enterprises.
Accordingly:
- If the newly established company remains classified as a FIE, the Catalogue of Encouraged Industries for Foreign Investment should be consulted.
- If the newly established company is classified as a domestic enterprise, the Encouraged Catalogue for Western China can be referred to.
Trends and opportunities
The periodic update of the Encouraged Catalogue for Western China reflects China’s strategic focus on leveraging regional strengths and promoting high-quality development. The 2025 edition highlights opportunities in renewable energy, medical technologies, advanced manufacturing, and Information and Communication Technologies (ICT), along with emerging markets like AI, green technologies, and the low-altitude economy.
Renewable energy
The Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025 emphasizes renewable energy development across multiple provinces, signaling a shift toward sustainability and green energy innovation.
- Offshore wind power: Guangxi’s focus on manufacturing offshore wind power equipment and subsea cables reflects a growing trend in utilizing coastal resources for renewable energy. This aligns with China’s new priorities for carbon neutrality and green infrastructure.
- Photovoltaic and energy storage: Provinces like Guizhou and Yunnan are ramping up R&D and manufacturing in solar power technologies, advanced energy storage systems, and battery recycling. Industries in these regions can take advantage of being key players in the national renewable energy supply chain.
- Green hydrogen and biomass: Qinghai is encouraging green hydrogen production and hydrogen pipeline infrastructure, while Inner Mongolia explores biomass technologies, addressing the need for diversified energy sources.
Medical technologies and services
Many regions in Western China are enriched by their traditional Chinese medicine and also encouraging medical technology innovation such as:
- Pharmaceutical R&D: Ningxia is focusing on treatments for major diseases like cancer and cardiovascular conditions, and Chongqing is advancing research in radiopharmaceuticals and artificial organs.
- Medical devices: Chongqing also leads in developing in vitro diagnostics and point-of-care testing (POCT) devices, essential for modern healthcare services.
- Health-tech integration: The manufacturing of oxygen supply equipment in Tibet and AI-powered healthcare applications in Yunnan demonstrate the region’s alignment with global health-tech trends.
The Chinese government is actively encouraging the development of the medical field in the Western Region for several strategic reasons. First, the region faces significant challenges in healthcare resource distribution, with gaps in service availability and quality compared to China’s more developed regions. By advancing the medical industry, the government aims to address these inequities, enhance healthcare outcomes, and ensure equitable access to medical services for all citizens.
Moreover, fostering medical innovation in the region can drive technological advancements, attract high-level talent, and build an ecosystem conducive to innovation and commercialization of cutting-edge medical advancements.
Beyond improving healthcare resource allocation, the government’s push to develop medical technologies and services in the Western Region is also economically motivated. Investment in the medical industry can stimulate economic activity, generate employment, and support related industries such as biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, and medical equipment manufacturing. This initiative aligns with efforts to diversify the region’s economy, reducing its historical reliance on resource-based industries.
Advanced and high-performance technologies
The Encouraged Catalogue for Western China 2025 highlights the growing emphasis on R&D and manufacturing of high-performance and advanced technologies:
- Aerospace innovations: Provinces like Guizhou are focused on high-temperature alloys for nuclear and aerospace applications, and Shaanxi prioritizes commercial aerospace technologies and drones.
- Special materials and alloys: Shaanxi and Gansu are advancing production in titanium, zirconium, and electronic-grade hydrofluoric acid for strategic industries. These developments cater to sectors like defense, semiconductors, and renewable energy.
- Green manufacturing: The adoption of technologies using natural gas and hydrogen to replace coal in metal smelting and chemical production reflects a shift toward low-emission industrial processes in Gansu and Qinghai.
In the information and communication technology (ICT) sector:
- Artificial intelligence: Yunnan and Tibet are fostering AI research, including generative AI and large-scale AI models, reflecting China’s intention of promoting R&D in AI development on a large scale.
- Low-altitude economy: Inner Mongolia’s focus on the low-altitude economy, including short-distance transportation and aviation equipment, opens new opportunities for drones and general aviation.
- Metaverse and IoT: Guangxi’s inclusion of the Metaverse and IoT technologies highlights the integration of immersive digital environments with real-world applications, offering the potential for innovation in entertainment, education, and logistics.
China’s strategy to encourage the development of high-performance technology and ICT in the Western region aligns closely with its national objectives for balanced regional development, technological self-reliance, and industrial upgrading. This focus supports broader strategic goals of achieving high-quality economic growth, fostering innovation, and ensuring the nation’s technological and economic resilience. In addition, the western region offers vast land resources, relatively lower operational costs, and growing infrastructure development, such as green energy production, which can support energy-intensive high-tech industries.
The impact of the CIT incentives on Western China
The implementation of preferential CIT policies for Western China has yielded remarkable results in recent years. Between 2021 and 2023, tax reductions exceeding RMB 400 billion (approximately US$55 billion) have supported local enterprises and attracted significant domestic and foreign investment. These measures have bolstered confidence in businesses and facilitated the development of strategic and emerging industries, such as electronics, equipment manufacturing, and biopharmaceuticals. As a result, the region has developed nine strategic industrial clusters, and five advanced manufacturing clusters tailored to its strengths.
These incentives have also fueled substantial economic growth in the western provinces. By 2023, the region recorded a 5.5 percent GDP growth rate and a 6.1 percent increase in industrial output, both outpacing national averages. This growth underscores the Western Region’s growing contribution to China’s economy and its improving per capita income levels, positioning it as an increasingly attractive destination for long-term investment.
Also Read:
- China’s 2024 Catalogue for Guiding Industry Restructuring
- Decoding China 2024 Green Industry Catalogue: Key Takeaways
- China Further Expands the Encouraged Catalogue to Boost Foreign Investment
About Us
China Briefing is one of five regional Asia Briefing publications, supported by Dezan Shira & Associates. For a complimentary subscription to China Briefing’s content products, please click here.
Dezan Shira & Associates assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Haikou, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. We also have offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Dubai (UAE) and partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh, and Australia. For assistance in China, please contact the firm at china@dezshira.com or visit our website at www.dezshira.com.
- Previous Article China-Sweden Economic Relations: Trade, Investment, and Opportunities
- Next Article Financial Analysis and Cost Audits: Identifying Cost Inefficiencies