China’s Jing-Jin-Ji Industrial Cluster: Sector Prospects and Policy Updates
China’s Jing-Jin-Ji industrial cluster plan aims to foster the growth of a world-class and evenly developed industrial ecosystem in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region. We discuss the progress made in the cluster’s constituent areas, gaps in regional growth, major and niche sectors offering investment potential for foreign enterprises, and the planned targets for 2025.
In May 2023, China unveiled the New Implementation Plan for Coordinated Development of Industries in Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Region (commonly referred to as “Jing-Jin-Ji” based on the Chinese abbreviations), which aims to foster the growth of world-class industrial clusters in area. This strategic plan prioritizes emerging sectors, such as electric vehicles, biopharmaceuticals, hydrogen energy, industrial internet, high-end industrial machinery, and robotics, in order to elevate China’s global competitiveness.
This article provides an overview of the progress of the Jing-Jin-Ji coordinated development plan, highlights the notable achievements, and explores the opportunities available for foreign direct investment (FDI) in the region.
What is the Jing-Jin-Ji coordinated industrial development plan?
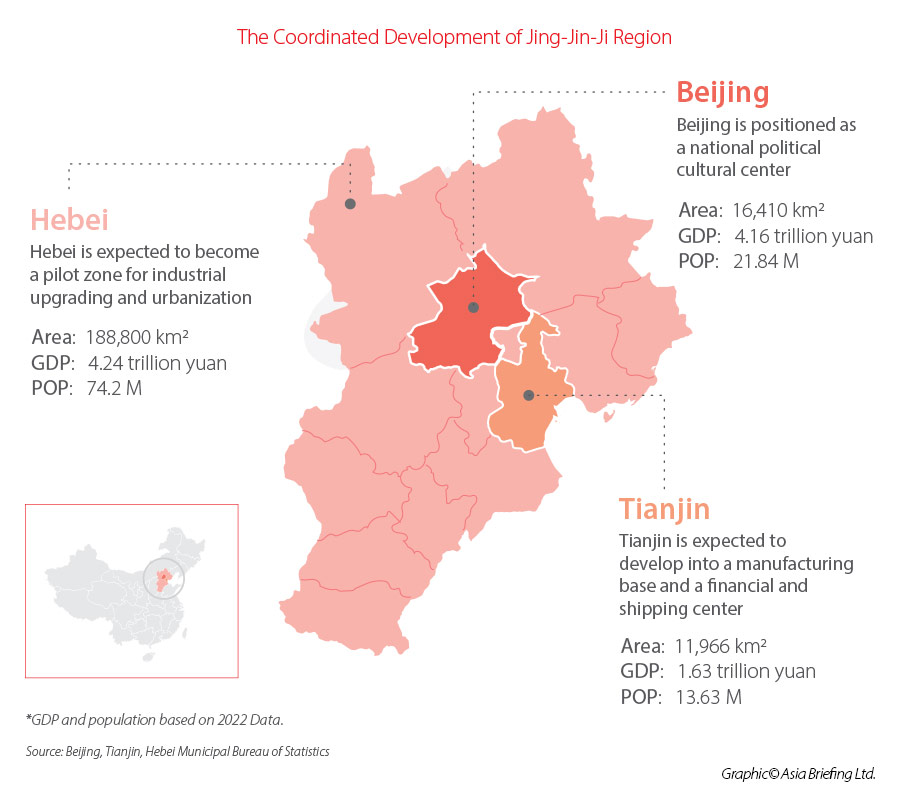
The coordinated development of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region is a national strategy put forward by President Xi Jinping in February 2014, to achieve better integration and more balanced development in the region. The plan seeks to address regional income disparities and reduce pollution levels while promoting economic growth and innovation.

According to the latest data, the Jing-Jin-Ji area has witnessed significant growth in its development index, recording an impressive nearly 39 percent increase from 2014 to 2021. In 2021, the development index of the region reached 138.9, indicating a notable improvement of 7.7 points compared to the previous year. These positive trends highlight the promising prospects and untapped potential of the Jing-Jin-Ji area.
The evaluation index system for the development of the Jing-Jin-Ji region is built on the basis of five development indicators, which include innovation, coordination, green development, openness, and shared development. Further information about the index is available here.
Achievements recorded in the Jing-Jin-Ji coordinated development
In recent years, the coordinated industrial development of the region has achieved landmark results.
Steady progress in coordinated growth
As of the end of 2022, the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region achieved significant growth in its industrial sector. The industrial added value reached RMB 2,511.44 billion (approx. US$353.97 billion), which is 1.5 times the value in 2013. This indicates an average annual growth rate of 4.5 percent.
Moreover, the total GDP of the region reached an impressive milestone of RMB 10 trillion (approx. US$1.41 trillion). Among the three areas, Beijing accounted for 42 percent of the total GDP, followed by Hebei with another 42 percent, and Tianjin with 16 percent. This distribution reflects the contribution of each area to the overall economic performance of the region.
Within the Jing-Jin-Ji area, there has been a significant development and cultivation of specialized small- and medium-sized enterprises known as “little giant” firms. These enterprises, numbering over 1,100, operate in niche sectors like technology promotion and application services, specialized equipment manufacturing, and instrument and apparatus manufacturing. They possess substantial market share and demonstrate strong innovative capabilities. These little giant enterprises in the Jing-Jin-Ji area represent 12.3 percent of the total number of similar enterprises nationwide.
Additionally, the collective efforts of enterprises from Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei have resulted in the establishment of over 90,000 branch and subsidiary companies within the Jing-Jin-Ji area. This widespread presence showcases the extensive reach and collaborative nature of businesses in the region.
Industrial layout optimization
Since 2014, Beijing has made remarkable strides in its commitment to environmental sustainability by effectively eliminating close to 3,000 general manufacturing and polluting enterprises. This concerted effort has resulted in a cleaner and more sustainable industrial landscape in the city.
Tianjin has been actively building a modern industrial system led by intelligent technology industries. It has achieved notable progress with a cumulative total of 77 national-level enterprise technology centers, ranking third among major cities in the country.
In Hebei, significant accomplishments have been realized through extensive industrial transformation and upgrading initiatives. The proportion of manufacturing units in the region has surged from 54.6 percent in 2014 to an impressive 79.3 percent in 2021. This substantial increase underscores Hebei’s commitment to enhancing its industrial capabilities and aligning with evolving market demands.
Accelerated capacity of industrial construction
To enhance its industrial capacity, the Jing-Jin-Ji region has strategically established five economic development zones (EDZs): Caofeidian Zone, Daxing International Airport Economic Zone, Zhangjiakou-Chengde Ecological Function Zone, and Binhai New Area. These zones have played a pivotal role in fostering industrial growth and collaboration.
Further, there are a total of 45 national new industrialization demonstration bases in the Jing-Jin-Ji region. These bases, built in EDZs, serve as vital drivers for promoting technological advancement, innovation, and the convergence of industries.
Boosted 5G network capacity
By the end of 2022, the Jing-Jin-Ji region had successfully deployed an extensive network of 205,000 5G base stations, ensuring comprehensive 5G network coverage across all urban areas, including prefecture-level and county-level cities. This widespread infrastructure has facilitated seamless connectivity and accelerated the digital transformation of the region, enabling businesses to benefit from the advantages of high-speed and reliable 5G technology.
Challenges ahead for Jing-Jin-Ji’s coordinated development
Despite the achievements introduced above, according to the latest annual report of Jing-Jin-Ji metropolitan region development, there are still significant challenges that need to be addressed.
Disparities in development among the three regions
In terms of economic development, the per capita GDP of Hebei Province in 2022 was only 29.9 percent of that of Beijing and 47.9 percent of that of Tianjin. In terms of education, healthcare, and other livelihood resources, Beijing significantly surpasses Tianjin and Hebei. Regarding industrial structure, there are noticeable differences in the development of the tertiary industry among the regions, particularly with Hebei still significantly lagging behind Beijing and Tianjin.
Difficulties in the coordinated environmental governance of the region
The current total emissions of air pollutants in the Jing-Jin-Ji region still exceed the environmental capacity. The overall carbon emissions of the Jing-Jin-Ji urban agglomeration show an upward trend, with evident regional imbalance. In 2022, Hebei accounted for 61 percent of the total carbon emissions in the Jing-Jin-Ji region. The carbon emission intensity of Jing-Jin-Ji as a whole is higher than the national average.
Slow progress in the development of green and digital economies
Government spending, research and development expenditure, and technological innovation in the Jing-Jin-Ji region have relatively limited promotion of the green economy, and a connected industrial chain for the green economy has yet to be formed. The region lacks dominant influence and impact in the global digital economy governance system. The supply of digital talents needs to be increased, and the aggregation of high-end digital talents on a global scale needs improvement.
Less effective institutional mechanisms for coordinated development
In the process of coordinated development, Jing-Jin-Ji still faces issues related to administrative systems, benefit distribution, policy regulations, and the sharing of government information. For example, there are disparities in the construction of government and open public data platforms among the three regions of Jing-Jin-Ji, and a lack of integrated mechanisms for coordinating data resources.
Key targets and tasks by 2025
According to the 2023 Implementation Plan, by 2023, the Jin-Jin-Ji region aims to achieve the following significant goals – advancing the region’s comprehensive strength to a higher level, fostering breakthroughs in collaborative innovation, continually enhancing the modern industrial system, and cultivating competitive advanced coordination system. These concerted efforts aim to enhance the region’s pivotal role in driving high-quality development in Jing-Jin-Ji.
The 2023 Implementation Plan also puts forward eight key tasks:
Optimize regional industrial division and productivity layout
The focus lies on optimizing the industrial division and positioning of Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei to support the development of advanced manufacturing clusters in the region, establishing cross-regional collaboration mechanisms, and strengthening regional coordination and policy synergy.
Enhance the advanced level of industrial foundation and industrial chains
Efforts are directed towards enhancing the advanced level of the industrial foundation and industrial chains through deepening regional collaboration in key sectors, such as new energy vehicles, biopharmaceuticals, and the industrial Internet. This includes establishing monitoring and collaborative mechanisms for key nodes in the supply chain to enhance the resilience and competitiveness of the industrial chain.
Enhance the regional industrial innovation system
It aims to promote the construction of open innovation carriers, key laboratories, and a cross-regional science and technology innovation ecosystem, as well as accelerate the transformation and application of innovation achievements.
Collaboratively build new advantages in the digital economy
It involves improving the new information infrastructure, coordinating the deployment of 5G networks and gigabit optical networks, and accelerating the deployment of the next-generation Internet based on IPV6 technology.
Accelerate green and low-carbon transformation
The key is to support the construction of a green manufacturing system in the region, develop a batch of green products, build green factories, and create national-level green parks. Meanwhile, the implementation plan aims to strengthen industrial energy conservation and emissions reduction.
Promote the integration of quality, branding, and standards
This involves improving the regional quality management system and expediting the establishment of a quality control system based on digitalization, networking, and intelligent technologies. The aim is to promote the adoption of a quality management approach that encompasses the entire industry chain and product lifecycle.
Cultivate and strengthen a group of high-quality enterprises
It supports enhancing the competitiveness of industry-leading enterprises in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei region, encouraging vertical integration of industry, innovation, and value chains, and promoting diversified industrial cooperation models. Through initiatives, such as “Hand-in-Hand Action,” it guides large enterprises to open up innovation resources to SMEs in the region.
Deepen high-level industrial openness and cooperation
It prioritizes deepening cooperation with neighboring regions, the Yangtze River Delta, the Guangdong-Hong Kong-Macao Greater Bay Area, and other key areas. This involves strengthening cross-regional industrial interaction, technological cooperation, market integration, project coordination, and information sharing.
Prospective FDI opportunities in Jing-Jin-Ji area
International trade and FDI inflow in the Jing-Jin-Ji area have continuously grown. In 2022, the total import-export value reached RMB 5.05 trillion (approx. US$710 billion), marking a year-on-year growth of 13.74 percent. The actual utilization of foreign investment in Beijing, Tianjin, and Hebei amounted to US$17.41 billion, US$5.95 billion, and US$1.66 billion, respectively, with year-on-year growth rates of 12.7 percent, 10.4 percent, and 7.6 percent respectively. These figures reflect the favorable investment climate and economic prospects.
Based on the coordinated development plan, Beijing has consistently provided robust support for the expansion of high-end industries, actively fostering innovation across various sectors. Within sectors like new generation information technology, healthcare, integrated circuits, and intelligent vehicles, there are several noteworthy opportunities for FDI. This is particularly due to Beijing’s substantial backing and the scope for technological advancements.
Likewise, Hebei province offers excellent prospects for FDI in industrial upgrading, with a particular focus on high-end equipment manufacturing, new energy, and modern logistics. Foreign investors can take advantage of the opportunities arising from Hebei’s push for industrial advancement, thereby capitalizing on the region’s potential for economic development. Tianjin city holds strategic significance as it strives to establish itself as a prominent financial and shipping hub.
Collectively, the convergence of Beijing’s support for high-end innovation, Hebei’s focus on industrial upgrading, and Tianjin’s aspirations for financial and shipping prominence provides a conducive environment for FDI and offers potential opportunities for investors seeking to participate in China’s growth and development.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, Dubai (UAE), and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article British Businesses in China: Conditionally Optimistic for 2023
- Next Article IASB Allows Temporary Exception to Reporting Requirements for Deferred Taxes Related to BEPS 2.0