China’s Machine Tool Industry: Market Trends and Opportunities
China’s machine tool industry, boasting a market value exceeding RMB 200 billion (approximately US$27.86 billion), relies significantly on foreign imports, driving diverse opportunities for international collaboration and investment, and supported by substantial government incentives.
China’s machine tool industry is the world’s largest, boasting a market value exceeding RMB 200 billion (approximately US$27.86 billion). Spearheaded by less than 20 high-end manufacturers, China has embraced advanced technologies, prioritizing the development of precise, intelligent Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machine tools and accessories.
Despite strong support from the government for the development of the domestic machine tool industry, the Chinese reliance on imported high-end CNC machine tools and accessories remains high, driving continued demand for foreign products.
Consequently, foreign manufacturers and suppliers are discovering ample opportunities for collaboration, capitalizing on China’s relentless pursuit of technological prowess and refined manufacturing standards.
This article provides an industry overview and lays out the diverse opportunities and challenges for investors. Foreign companies will gain key insights into China’s machine tool industry—dominant market leaders, trends in technology development, and relevant regulations impacting business and R&D.
What are machine tools?
Machine tools, also known as industrial machines, are machines that can process metal blanks into machine parts and manufacture machines. They are widely used in the traditional machinery industry, mold industry, automotive industry, electric power equipment, railway locomotives, shipbuilding, aerospace industry, and various other sectors. The machine tool industry refers to the sector within the economy that is involved in the manufacturing, distribution, and sale of various tools and equipment utilized in industrial operations and processes.
Overview of China’s industrial machinery sector
China’s machine tool industry is a dynamic and vital sector that forms the backbone of the country’s manufacturing, construction, and maintenance activities. This industry encompasses the production and distribution of a wide array of tools, equipment, and components designed to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and safety across various industrial applications.
Within this industry, tools are categorized based on their intended applications, leading to various subsectors, including tools for general purposes, those designed for the construction sector, everyday utility tools, hardware related to locks and abrasives, kitchen and bathroom fixtures, household hardware, and essential metal components.
Industry demand and production
Reflecting China’s robust demand for mechanical processing, the country’s machine tool consumption represents a significant 32 percent of the global market share. This surge in demand aligns with the rapid expansion of the domestic manufacturing sector, which explains China’s position as the largest machine tool market globally.
In 2020, China’s production of metal-cutting machine tools surged to 446,000 units, a noteworthy 5.9 percent year-on-year (YoY) growth. Meanwhile, the production of metal-forming machine tools slightly decreased to 202,000 units, marking an 8.6 percent YoY decline.
The year 2021 witnessed a robust revival in production, driven by the ongoing post-pandemic recovery and the gradual enhancement of both domestic and international economic conditions.
However, in 2022, amid varying circumstances in the global economy, the machine tool industry faced subdued demand from end-users, resulting in the production of 572,000 units for metal-cutting machine tools and 183,000 units for metal-forming machine tools.
Key industry players and market leaders
The machine tool industry in China is notably competitive, characterized by a vibrant landscape that is constantly evolving with advancements in technology and innovation. Both local and foreign players are actively engaged in a race to deliver cutting-edge solutions, pushing the boundaries of precision engineering and efficient manufacturing.
Key local players include, among others:
- Shenyang Machine Tool Co., Ltd;
- Dalian Machine Tool Group Corporation;
- Qiqihar No.2 Machine Tool Group Co., Ltd;
- Nanjing No.1 Machine Tool Works; and
- Jinan No.1 Machine Tool Co., Ltd.
Notable foreign industry players are:
- DMG Mori;
- Trumpf;
- Amada;
- Mazak; and
- Okuma.
Import-export dynamics
In the context of the machine tool industry in China, it is necessary to look into the import-export dynamics. Given the country’s heavy reliance on imported machine tools, the trade landscape plays a crucial role in shaping the sector.
China, as a major global manufacturing hub, often relies on imported high-end machine tools to meet the demand for advanced technology and specialized equipment. Consequently, the import and export of machine tools serve as key indicators of the industry’s technological advancement and global competitiveness.
According to data released by the General Administration of Customs of China, the total import value of machine tools reached US$8.24 billion in 2021, marking a 24.9 percent increase compared to the previous year. However, in 2022, the total import value of machine tools in China was US$7.16 billion, reflecting a decrease of 13.1 percent year-on-year.
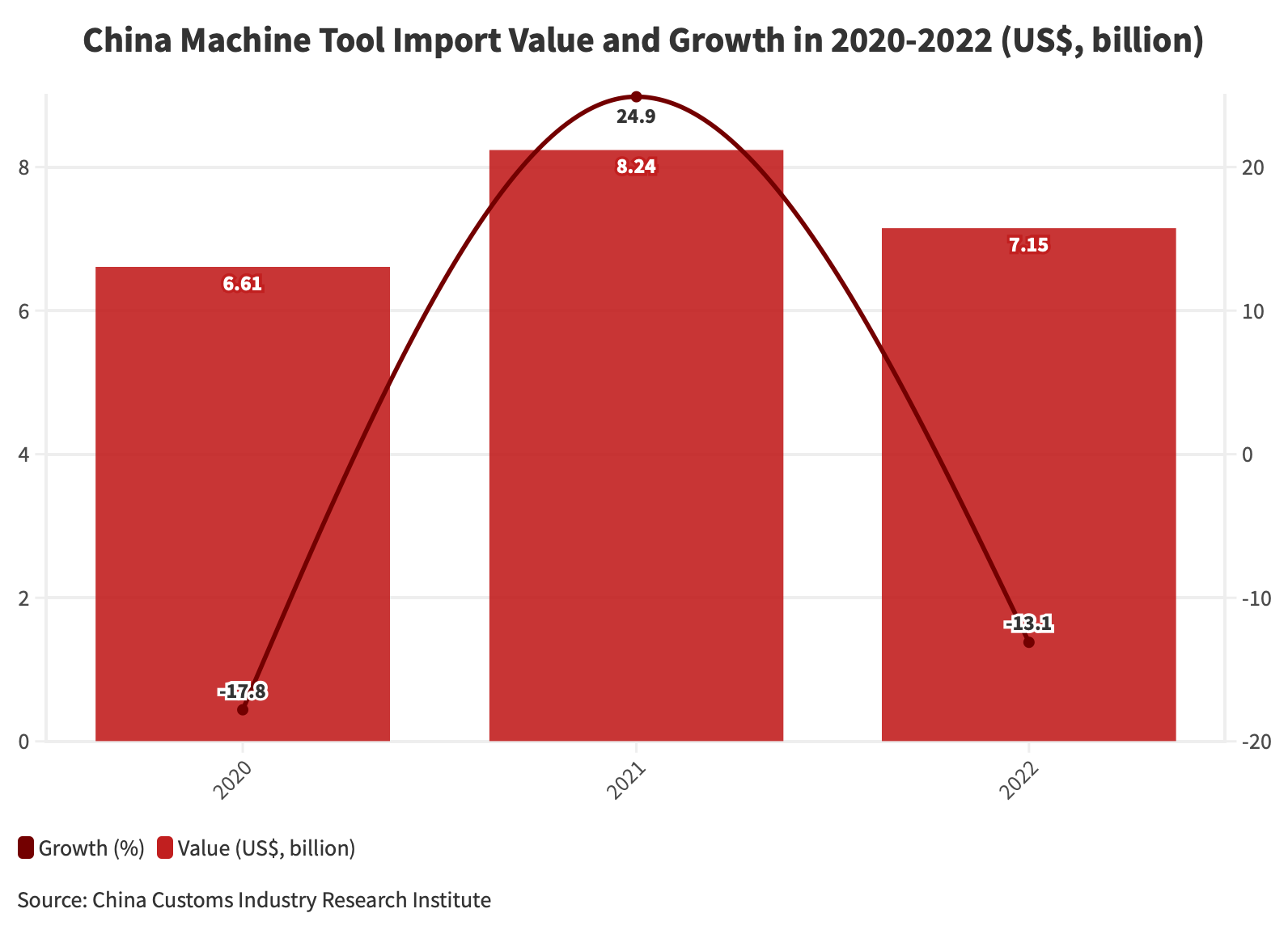
Regardless of the periodic flux in trade, it is worth noting that the Chinese medium and high-end machine tools industry heavily relies on exports from Asian and European countries. This is attributed to the lower localization rate in this segment, which stands at less than 10 percent. In 2021, the average price of machine tools exported from China was approximately US$300 per unit, while the average import price was significantly higher at US$76,700 per unit.
Analyzing the field of application for domestically produced low-end CNC machine tools, the automotive sector holds a big share, comprising 40 percent of the total, with the aerospace, mold, and construction machinery industries contributing 17 percent, 13 percent, and 10 percent, respectively.
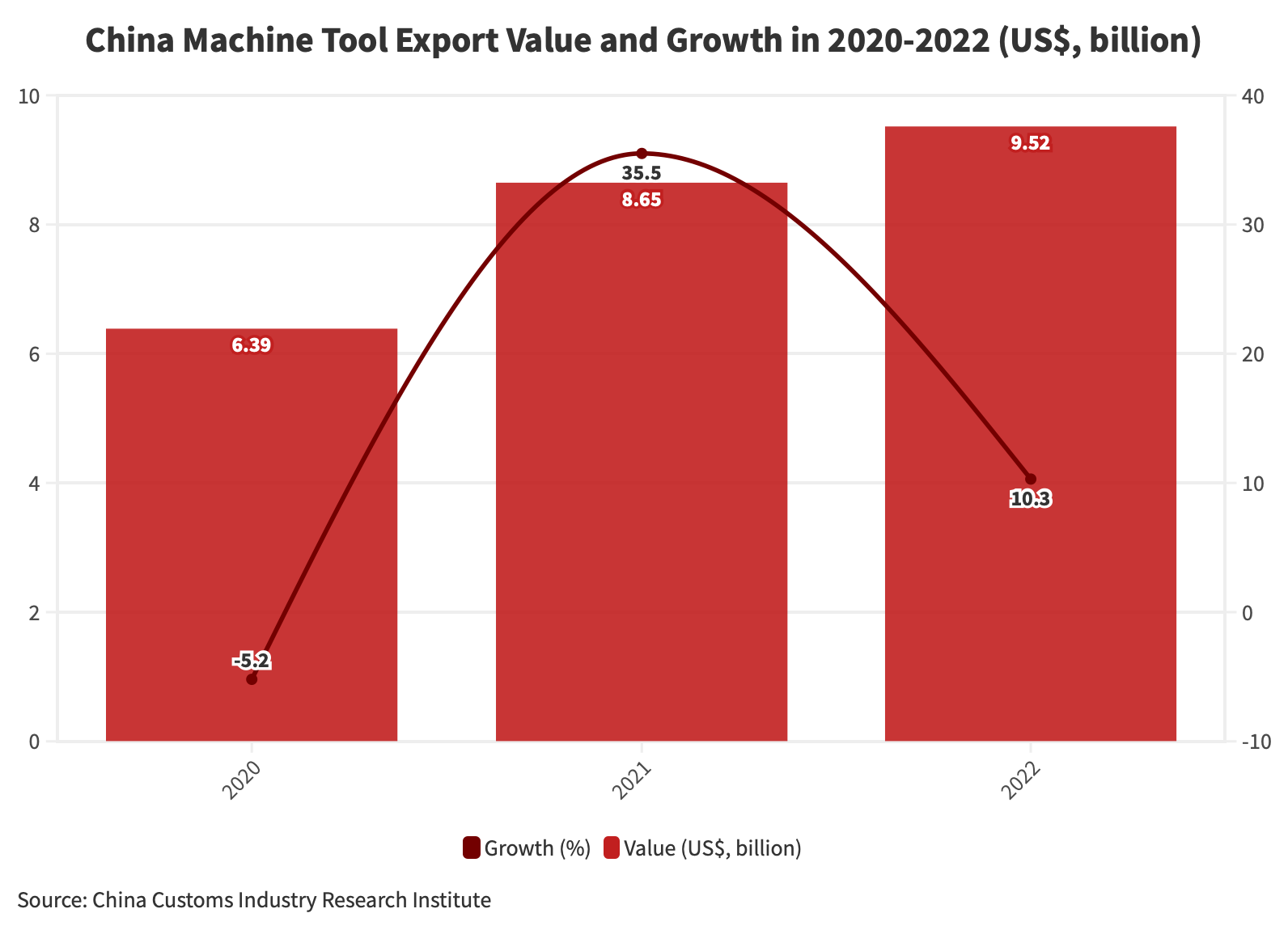
On the other hand, in 2022, China exported 20.87 million units of machines, a decline of 26.4 percent YoY. In contrast, the export value of China’s machine tools in 2022 reached US$9.5 billion, a growth of 10.3 percent YoY. The average export price of China’s machine tools in 2022 reached US$500 per unit, compared to US$300 per unit in 2021. This data highlights the significant shifts and trends within China’s machine tool export landscape.
Market trends
Automotive industry growth driving market demand
China’s automotive industry continues to experience substantial growth, propelled by a surge in demand for electric vehicles (EVs) and initiatives promoting sustainable transportation. Indeed, with an increasing focus on reducing carbon emissions, EVs are gaining significant traction, necessitating significant investment and generating employment opportunities.
As such, the Chinese government’s strong emphasis on electric and autonomous vehicles has created a robust market for cutting-edge machine tools catering to the evolving automotive production demands. For instance, renowned Chinese automakers like BYD and NIO have actively invested in advanced manufacturing facilities integrating CNC machines for enhanced production efficiency and quality control. The auto brands are also seeking better performance in export markets.
Dominance of CNC machine tools
The growing emphasis on automated manufacturing and the integration of 3D printing technologies with CNC machines are key trends in China’s industrial landscape. Chinese manufacturers, aiming for heightened competitiveness, are increasingly incorporating CNC machines into their production processes to streamline operations and minimize errors.
This is certainly the case with leading Chinese companies Huawei and DJI, who are investing in advanced CNC technologies to revolutionize their respective manufacturing capacity, allowing for multi-material capabilities and resource optimization.
Additionally, the integration of CNC machines in the power generation sector is gaining momentum, supporting China’s commitment to sustainable and efficient energy production. Leading Chinese energy companies, such as State Grid Corporation of China and China Huaneng Group, are actively deploying CNC machines in their power generation facilities to enhance automation and streamline operations, aligning with the nation’s broader energy conservation objectives.
Regulatory environment
China’s policies toward the machine tool industry have shown significant progress over the past four years. Before 2019, policies mainly provided general directions, including the establishment of CNC machine tool standards and the recognition of the sector as a strategic industry under the Made in China 2025 initiative. Since 2019, however, the regulatory framework has become more specific, with a heightened focus on strengthening the industry’s core technological capabilities.
In September 2021, the Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council emphasized the need to bolster key core technologies in the machine tool industry. In the same year, the 14th Five-Year Plan for Intelligent Manufacturing outlined support for the development of intelligent machining centers and high-precision CNC grinding machines.
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) has also been actively engaged, indicating ongoing top-level strategic planning for China’s machine tool industry. Such concrete policy measures reflect the government’s commitment to fostering an enabling environment that supports innovation and technological advancement within the machine tool sector.
Tax incentives
China has announced a series of tax incentives aimed at fostering growth and development within the industrial machine tool sector. These incentives, released by the Ministry of Finance (MoF), the State Taxation Administration (STA), the National Development and Reform Commission (NDRC), and the MIIT, include policies related to the additional deduction of value-added tax (VAT) and the super deduction of research and development (R&D) expenses.
Additionally, MIIT, along with other pertinent authorities, has introduced measures to regulate and monitor the eligibility of industrial machine tool enterprises for these tax incentives.
The below table provides a comprehensive overview of the key policies and their respective details.
|
Tax Incentives for the Machine Tool Industry in China |
|
| Policy | Details |
| Circular of the MOF and the STA on the Policies for Additional Deductions of VAT for Industrial Machine Tool Enterprises (Cai Shui [2023] No.25).
Available here |
|
| Announcement on Raising the Additional Deduction Proportion of R&D Expenses for Integrated Circuit Enterprises and Industrial Machine Tool Enterprises (MOF, STA, NDRC, MIIT Announcement [2023] No.44)
Available here |
|
| Circular on Matters Concerning the Preparation of the List of Industrial Machine Tool Enterprises Eligible for the Additional Deduction of Value-added Tax in 2023 (MIIT Announcement [2023] No.245)
Available here |
|
| Notice on the Implementation of the List of Industrial Machine Tool Enterprises Eligible for the Additional Deduction of R&D Expenses Policy in 2023 (MIIT Announcement [2024] No. 60)
Available here |
|
China’s push for self-sufficiency
In a strategic move toward self-reliance, China has steadily sought to decrease reliance on foreign technology, climb the value chain, and take the lead in developing precise, high-speed, and efficient CNC machine tools, as well as integrated manufacturing systems.
Made in China 2025, for example, emphasizes expediting R&D in cutting-edge technologies and equipment, especially focusing on high-end CNC machine tools and precision components.
In response to current geopolitical events, the Chinese government is intensifying efforts to curtail dependence on high-tech imports from the United States and pushing for greater domestic capabilities.
To support domestic CNC machine tools manufacturers, the Party committee of the Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council To support domestic CNC machine tools manufacturers, the Party committee of the Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council has underscored the vital importance of upgrading the entire domestic CNC machine tools industry chain. Additionally, they encourage state-owned enterprises (SOEs) to actively integrate themselves into the national framework for fundamental research, application, and innovation, focusing on the sector’s development.
Still, this proactive approach towards building up China’s machine industry prowess positions the country as a lucrative destination for foreign investors and businesses seeking opportunities in the realm of advanced manufacturing and technology and related industries.
Opportunities for foreign players
Amid the dynamic shifts within China’s machine tool industry, international companies are well-positioned to seize a range of opportunities. By fostering strategic partnerships and collaborating with local Chinese counterparts, they can engage in valuable technology transfer initiatives, facilitating the exchange of expertise in developing advanced CNC machinery and precision tools.
The evolving landscape of the Chinese manufacturing sector demands customized solutions tailored to specific market niches and requirements. Foreign exporters, recognizing this trend, can focus on providing bespoke products and services, thus effectively meeting the diverse and ever-evolving needs of local industries.
The growing emphasis on high-precision, intelligent CNC machines has triggered a surge in the demand for top-quality components and accessories. Foreign suppliers can tap into this trend by exploring the supply of critical components, effectively meeting the escalating market demands with their high-quality offerings.
As China pushes ahead with its technological advancements, foreign companies specializing in cutting-edge machine tool technologies and equipment upgrades will find a promising market for their services. By providing technological advancements and upgrade solutions, these companies can actively contribute to China’s technological journey. Furthermore, the emergence of newer segments within the machine tool industry, such as smart machining centers and precision grinding machines, presents a valuable opportunity for foreign exporters and enables a strong foothold in the market.
This article was first published on October 17, 2023, and last updated on March 7, 2024.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, Dubai (UAE), and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China Expanded Its 15-Day Visa-Free Travel Policy to 6 European Countries Including Switzerland
- Next Article Navigating Women’s Employment in China: Recent Advancements and Ongoing Challenges



























