China Extends NEV Tax Reduction and Exemption Policy to 2027
China has extended its tax exemption policy for new energy vehicles (NEVs) until 2027, showcasing its commitment to promoting the electric vehicle (EV) industry. This move is expected to boost domestic sales and maintain China’s position as a global leader in EVs. The extension provides stability and support for consumers and manufacturers, besides encouraging foreign investment prospects in electric mobility.
With more than half of the world’s electric cars and having already exceeded its 2025 target for new energy vehicles (NEVs) sales, China has become a global leader in the electric vehicle (EV) industry. To further boost domestic sales in this sector, the country has now announced an extension of its tax exemption policy for NEVs. The tax break, initially set to expire in 2023, will now be extended until 2027.
As this recent development signifies China’s commitment to fostering the growth of the strategic EV industry, we delve into the policy announcement and its implications for the sector.
China’s NEV purchase tax reduction policy
China has implemented various tax exemption and reduction policies to promote the adoption of NEVs, which include EVs, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), and fuel cell vehicles (FCVs).
Starting from September 2014, the Chinese government has exempted the 10 percent purchase tax on qualified NEVs. This exemption applies to both domestically produced NEVs and imported models. The purchase tax exemption, originally set to expire in 2020, was first extended to 2022 with the aim to support the market shaken by the COVID-19 pandemic, and then again extended in September 2022 to cover NEV purchases in 2023.
Updated tax exemption breakdown
On June 21, 2023, the Ministry of Finance (MOF), State Taxation Administration (STA), and Ministry of Industry and Information Technology (MIIT) jointly released the Announcement on Continuing and Optimizing the Vehicle Purchase Tax Reduction and Exemption Policy for New Energy Vehicles (hereinafter referred to as the Announcement).
As per the Announcement, the new tax exemption will come into effect on January 1, 2024, and remain in place until December 31, 2027. This four-year extension provides a more stable and predictable environment for consumers and manufacturers alike, encouraging them to invest in and embrace the transition toward electric mobility.
Under the extended policy, NEV vehicles purchased in China between January 1, 2024, and December 31, 2025, will be granted an exemption from the purchase tax amounting to as much as RMB30,00 (US$4,170) per vehicle.
However, starting from January 1, 2026, until December 31, 2027, the tax exemption will be halved, and the per-unit exemption amount will be capped at RMB15,000 (US$2,078), signaling a gradual reduction in government support.
This phased approach aims to maintain the momentum of the EV market while gradually shifting towards more self-sustaining growth.
Impact on the NEV market
The tax break extension for NEVs in China has generated considerable interest and speculation among industry experts and market participants. The decision holds significant implications for the country’s EV sales. Indeed, the Chinese government increasingly views electric mobility as a crucial pillar of its economy and the country’s green transformation, aligning with its broader goals of reducing carbon emissions, improving air quality, and enhancing energy security.
According to the International Energy Agency (IEA), China holds the title of being the largest market for electric cars worldwide, responsible for 60 percent of global electric car sales in 2022. In the same year, China witnessed a substantial surge in the sales of clean cars, reaching almost 5.67 million units, indicating a remarkable 90 percent growth compared to the previous year.
The Chinese government has been actively providing substantial incentives to buyers and offering subsidies to car manufacturers for over a decade, aiming to bolster the clean car sector. These efforts have attracted a significant number of companies to the Chinese auto market. At one stage, consumers could receive incentives of up to RMB60,000 (US$8,317) when purchasing an EV – until January 2023.
However, the overall economic slowdown in China has impacted the sector, where growth has also slowed down. While the vehicle purchase tax exemption policy for NEVs is extended, there is no indication of a renewal of cash subsidies for EVs.
Prospects for the EV market financial year are being tempered, as reflected by a slight easing in lithium prices.
Overall, assuming the discontinuation of new government subsidies, the share of EV cars is projected to marginally increase from 26 percent of all passenger cars in 2022 to 27.5 percent in 2023.
Recent data from the China Association of Automobile Manufacturers, however, paints a more optimistic view, revealing that passenger car sales in China reached their highest point in five months, totaling 2.05 million units in May 2023. Although electric vehicle sales were slightly below the peak recorded in December 2022, they still amounted to 717,000 units.
With the credit system and the tax exemption policy, citizens can directly benefit from reduced costs associated with purchasing NEVs. This direct advantage is expected to stimulate consumer interest and generate strong support for the EV market.
Boosting battery and raw materials demand
The tax exemption’s impact is not limited to the EV market alone; it is also likely to boost the demand for battery raw materials. As the adoption of electric vehicles increases, the need for batteries and their key components, such as lithium, nickel, and cobalt assets, will grow as well. This surge in demand for upstream battery raw materials will have a cascading effect on the related industries, including mining, refining, and manufacturing.
For five consecutive years, China has maintained its position as the largest consumer of lithium-ion (li-ion) batteries. Moreover, the Chinese battery market is projected to achieve a remarkable compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 7.5 percent from 2022 to 2027.
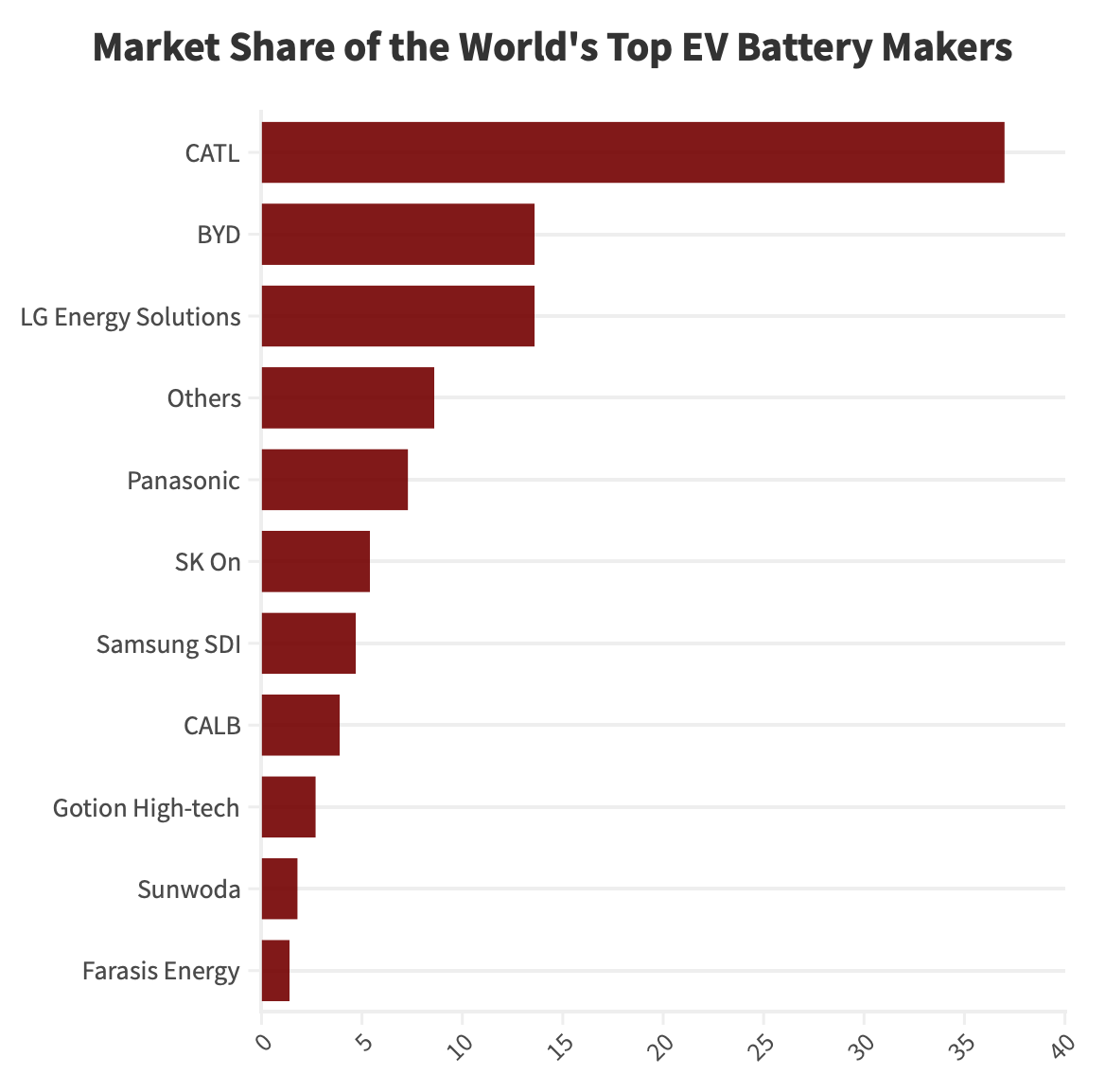
Indeed, the country’s dominance in battery production is unparalleled, with its leading battery manufacturer, Contemporary Amperex Technology Co. (CATL), holding approximately 37 percent of the global li-ion battery market in 2022. In fact, six out of the top 10 battery companies in the world were Chinese in 2022, highlighting China’s strong position and capacity in domestic production.
In the first five months of 2023, the prices of upstream battery raw materials, including lithium, nickel, and cobalt, have experienced downward trends. This can be attributed to limited demand primarily caused by sluggish sales in the EV market.
However, in May 2023, prices of lithium-ion batteries rose for the first time, as Chinese lithium carbonate prices surged 50 percent – a direct consequence of a recovery of the country’s EV market.
This signifies the natural link between the two sectors and a likely positive impact of the extended tax breaks on the batteries and raw materials market.
China’s strategic focus on the EV industry
China’s commitment to electric mobility is driven by multiple factors. First and foremost, the government aims to reduce the nation’s carbon emissions and mitigate the environmental impact of transportation. By promoting the adoption of NEVs, China can make significant strides toward achieving its ambitious climate targets.
Furthermore, the electric vehicle industry represents an opportunity for China to enhance its energy security. A major consumer of fossil fuels, China is keen to reduce its dependence on imported oil and transition towards domestically produced renewable energy sources. By embracing electric vehicles powered by clean energy, China can diversify its energy mix and reduce its reliance on foreign oil.
Additionally, the development of the EV industry aligns with China’s broader economic goals. The government recognizes that a thriving electric vehicle market can stimulate technological innovation, create new job opportunities, and drive economic growth. By nurturing the domestic EV sector, China aims to establish itself as a global leader in electric mobility and secure a competitive edge in the emerging clean transportation industry.
To achieve these goals, the Chinese government has demonstrated strong support for the electric car industry, beyond tax breaks and subsidies, emphasizing substantial investments in research and development.
The implementation of the NEV credit system in 2019 is one notable initiative in this supportive landscape. This system necessitates automakers to acquire credits by manufacturing and selling NEVs, including electric cars. Non-compliance with the annual NEV credit quotas results in penalties for automakers. Consequently, this credit system has incentivized automakers to invest in electric vehicle production while also compelling them to reduce emissions from their traditional gasoline-powered vehicles.
Another key priority for the government has been the establishment of a comprehensive charging infrastructure throughout the country. In 2015, a significant announcement was made to construct 12,000 charging stations and 8 million charging points by 2020. Surpassing these goals, China now boasts over 800,000 public charging stations available to the public.
Potential for growth in the future
Notwithstanding temporary slowdowns, the future of China’s EV industry looks bright.
The Chinese car market offers an advantage over Western car markets in terms of its continued growth trajectory and the increasing number of middle-class households opting for car ownership. Unlike saturated Western markets, the Chinese market still has room for expansion.
About Us
China Briefing is written and produced by Dezan Shira & Associates. The practice assists foreign investors into China and has done so since 1992 through offices in Beijing, Tianjin, Dalian, Qingdao, Shanghai, Hangzhou, Ningbo, Suzhou, Guangzhou, Dongguan, Zhongshan, Shenzhen, and Hong Kong. Please contact the firm for assistance in China at china@dezshira.com.
Dezan Shira & Associates has offices in Vietnam, Indonesia, Singapore, United States, Germany, Italy, India, and Russia, in addition to our trade research facilities along the Belt & Road Initiative. We also have partner firms assisting foreign investors in The Philippines, Malaysia, Thailand, Bangladesh.
- Previous Article China Reopening in 2023 – What’s Changed in the Economy, Policy, and Diplomacy?
- Next Article Trademark Registration in Hong Kong: A Primer